| What
is set forth on this page is but a tip of the iceberg of the
comprehensive laws of estate taxation. It is a mere glimpse
of some of the basic tax planning rules to reveal to you just
how important it is to get good legal advice to ensure you
minimize your estate tax bill.
The basic rules:
Federal Gift and Estate Tax Lifetime Credit for 2015:
$5.43mm/person. Over and above this lifetime credit, a
gifter may gift any numerous people what is call the annual
exclusion amount, which is $14,000/per gifter/per donee.
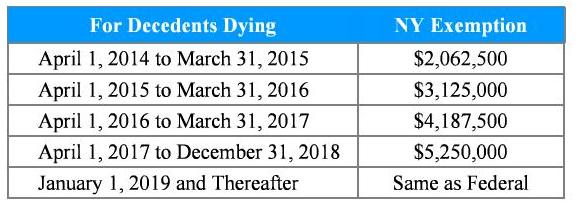
Please be aware, that there is a separate New York
Estate tax that is in effect, over and above the Federal
Estate tax.
But...there are ways to give way more during your lifetime
Of course, to every basic rule, there is an exception,
here are a few:
- $14,000 exclusion. Every year, a person may give any
number of people $13,000 each. Jointly, a married couple
may give each person $26,000. The benefits include reduction
of your taxable estate, and this $13,000 does not use
up any of your lifetime credit.
- Spousal Allowance. If your spouse is a United States
citizen, you may give your spouse thousands, millions
or billions of dollars tax free. Again, this does not
use up any of your lifetime credit. The problem arises
when your spouse dies, and the money goes to others. The
money will be fully taxable. ** Speak to an attorney if
your spouse is not an American citizen, special rules
apply.
- If your estate is greater than the credit allowed, it
would be wise to divide your assets between you and your
spouse, held in separate names, so you can utilize and
maximize each of your lifetime credits.
- Charitable Allowance. You can give an unlimited amount
of money to charities tax-free. Your attorney will advise
you as to whether your charity is a tax-exempt corporation
which allows deductibility.
- Start a trust for the benefit of your children or grandchildren's
health, education, maintenance and support.
- Pay for any person their medical, dental, tuition or
rent bill, PROVIDING, you pay directly to the provider
and not to the beneficiary
There are other means and variations of the above which
will help you accomplish your goals. Your attorney will
help you based on your special facts and circumstances.
Helpful Links
New York State Tax Forms:www.tax.state.ny.us/forms
Internal Revenue Service Tax Forms:www.irs.gov/forms_pubs
Definitions:
Taxable Estate:
That property which is subject to taxes. Please understand
that even if you did not have a probate estate, your estate
can still be a taxable estate. It includes, among other
things, property which was held jointly, insurance policies,
houses, bank accounts, brokerage accounts and gifts that
were given by the deceased person within three years of
his death.
bullet
Probate Estate: Only that property which
the decedent owned in his own name only, or as a tenant
in common with someone else. Those assets held jointly with
the right of survivorship or by the entirety (special only
to married couples), by operation of law automatically run
to the joint owner, and need not go through probate. Please
note that although said joint property does not have to
go through probate, the entire value of the joint property
is placed as if the first to die owned it entirely and taxes
have to be paid on the entire value of the asset.
bullet
Lifetime estate tax credit: It is the
total amount of money which the government allows you to
transfer in your lifetime and at death tax-free.
bullet
Stepped up basis: The fair market value
of the decedent's assets as of the time of his death, versus
the value of the assets at the time the decedent purchased
said assets or was gifted said assets.
Go to the top of the
page |